As we age, our bodies undergo various changes, including a natural decline in muscle mass and strength. This age-related loss of muscle, known as sarcopenia, can significantly impact the health and independence of older adults. Sarcopenia not only affects mobility and functionality but also increases the risk of falls, fractures, and other health complications. However, there is hope. Research has shown that engaging in regular strength training exercises can play a crucial role in preventing and even reversing sarcopenia. By incorporating strength training into their routine, individuals over 60 can maintain muscle mass, improve strength, and enhance overall quality of life.
In this article, we will explore the significance of strength training for older adults in combating sarcopenia. We’ll delve into the science behind sarcopenia, discuss the benefits of strength training, and provide practical tips and exercises to help individuals over 60 stay strong, active, and independent. Let’s embark on a journey to preserve muscle health and vitality as we age.
Understanding Sarcopenia
Sarcopenia, derived from the Greek words “sarx” (flesh) and “penia” (loss), refers to the age-related decline in skeletal muscle mass, strength, and function. As individuals age, they naturally experience a gradual loss of muscle mass and strength, but sarcopenia represents an accelerated and pathological form of this process. It is a multifactorial condition influenced by various physiological, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Sarcopenia is a common condition among older adults, particularly those over the age of 60, with prevalence increasing with age. Several factors contribute to its development, including age-related hormonal changes, chronic diseases, inactivity, inadequate nutrition, and inflammation. The hallmark symptoms include progressive loss of muscle mass, strength, and function, leading to weakness, reduced mobility, fatigue, and an increased risk of falls and fractures. Sarcopenia is associated with adverse health outcomes, such as functional decline, disability, loss of independence, and increased mortality risk. Diagnosing sarcopenia involves a comprehensive assessment of muscle health using various tools and techniques. Understanding sarcopenia is crucial for promoting healthy aging and preventing adverse health outcomes among older adults, emphasizing the importance of interventions like strength training and nutritional support to maintain optimal muscle health and function.

Benefits of Strength Training for Seniors
Strength training is not just about building muscles; it’s a holistic approach to enhancing the health and vitality of seniors aged 60 and above. By engaging in regular strength training exercises, older adults can experience a wide range of benefits that extend beyond physical fitness. From improving cardiovascular health and bone density to boosting cognitive function and mental well-being, strength training offers a comprehensive solution to age-related health concerns. Additionally, it fosters a sense of independence and empowerment, enabling seniors to maintain an active lifestyle and enjoy a higher quality of life as they age.
Increased Muscle Mass and Strength
Strength training for seniors facilitates the preservation and augmentation of muscle mass and strength, crucial for maintaining mobility, independence, and quality of life as individuals age.
Enhanced Balance and Coordination
Regular strength training exercises contribute to improved balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and associated injuries, common concerns for older adults.
Improved Bone Density and Osteoporosis Prevention
Engaging in strength training stimulates bone growth and density, lowering the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, thus promoting better bone health among seniors.
Better Metabolic Health and Weight Management
Strength training supports metabolic health and weight management by boosting metabolism, increasing energy expenditure, and facilitating fat loss while preserving lean muscle mass.
Enhanced Mood and Psychological Well-being
Beyond physical benefits, strength training has positive effects on mental health, reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety, and promoting overall psychological well-being among seniors.
Improved Cardiovascular Health
Regular resistance training sessions can help lower blood pressure, improve blood circulation, and reduce the risk of heart disease, contributing to overall cardiovascular well-being in older adults.
Designing a Strength Training Program for Seniors
Creating a strength training program for seniors requires careful consideration to ensure safety, effectiveness, and enjoyment. Here are key factors to consider when designing a program:
Assessing Fitness and Medical Levels
Before starting a strength training program, it’s crucial to assess the individual’s current fitness level and any existing medical conditions. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a certified fitness trainer can help tailor the program to meet specific needs and avoid potential risks.
Setting Realistic Goals
Establishing clear, realistic goals is essential for motivation and progress. Goals might include improving muscle strength, increasing flexibility, enhancing balance, or simply maintaining overall health and well-being.
Progressive Overload
To continue making gains in strength and muscle mass, it’s important to gradually increase the resistance or weight used in exercises. This progression should be done carefully to avoid overexertion and injury.
Recommended Exercises for People Over 60
When designing a strength training program for seniors, it’s important to choose exercises that are safe, effective, and tailored to their specific fitness levels. Here are some recommended exercises:
1. Bodyweight Squats
Bodyweight squats are an effective exercise for strengthening the legs, glutes, and core, which are essential for maintaining mobility and stability as we age.
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart.
- Lower your body by bending your knees and pushing your hips back.
- Keep your chest up and your back straight throughout the movement.
- Return to the starting position.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.

2. Seated Leg Press
Seated leg press exercises are excellent for building lower body strength, particularly targeting the quads, hamstrings, and glutes, making it a beneficial exercise for maintaining leg strength and stability in seniors.
- Use a leg press machine.
- Sit down with your back against the seat.
- Place your feet on the platform.
- Push the platform away by extending your legs.
- Return to the starting position by bending your knees.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.

3. Standing Leg Lifts
Standing leg lifts are effective for improving balance and strengthening the hip muscles, essential for maintaining stability and preventing falls in seniors.
- Stand behind a chair for support.
- Lift one leg to the side, keeping it straight.
- Lower the leg back down.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
- Switch legs after completing a set.
4. Seated Shoulder Press
The seated shoulder press is an excellent exercise for targeting the shoulders and upper arms, enhancing upper body strength and stability.
- Sit on a chair with back support.
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder height.
- Press the weights overhead until your arms are fully extended.
- Lower the weights back down to shoulder height.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.

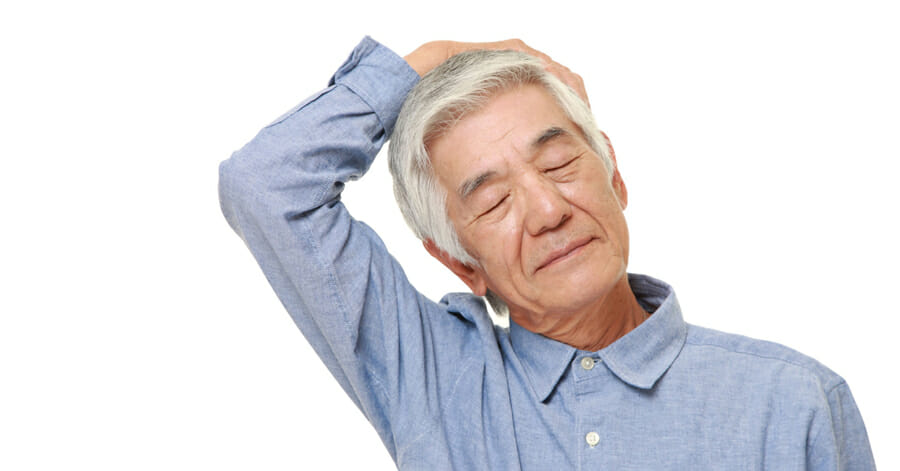
5. Neck Stretches
Neck stretches are beneficial for relieving tension in the neck and shoulders. To perform this exercise, follow these steps:
- Sit or stand with your back straight.
- Gently tilt your head to one side, bringing your ear toward your shoulder.
- Hold for a few seconds, then switch sides.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.

Conclusion
Strength training is a powerful tool in the fight against sarcopenia and the natural aging process. As we age, sarcopenia can lead to significant declines in muscle mass, strength, and overall function, impacting mobility, independence, and quality of life. However, engaging in regular strength training can help mitigate these effects by preserving muscle mass, enhancing strength, improving balance and coordination, and supporting bone health.
The benefits of strength training for individuals over 60 extend beyond physical improvements. It can boost metabolic health, support weight management, and positively impact mood and psychological well-being. By adopting a well-designed strength training program that includes exercises tailored to their needs, older adults can maintain their strength, reduce their risk of falls and fractures, and enjoy a higher quality of life.